KPI & Performance Tracking
This specialization focuses on understanding, defining, tracking, and reporting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure business, departmental, and individual performance in a structured and meaningful way.
Compare & Select from 100+
Best Universities for your KPI & Performance Tracking
100% Placement Assistance
???? Overview
In modern organizations, decisions are increasingly driven by performance data. Managers and leaders rely on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to understand whether teams, departments, and processes are performing as expected. KPIs help convert goals into measurable outcomes and provide a factual basis for reviews, planning, and corrective actions.
The KPI & Performance Tracking specialization is designed to help working professionals understand how KPIs are selected, tracked, analyzed, and reported as part of regular MIS and business reporting. The focus is not on advanced analytics or predictive modeling, but on practical performance measurement commonly used in corporate environments.
This specialization trains learners to think beyond raw numbers and focus on meaningful metrics. Learners develop the ability to identify what should be measured, how often it should be tracked, and how results should be presented to management in a clear and responsible manner.
KPIs are not just numbers on a report—they influence decisions related to targets, incentives, resource allocation, and process improvement. This specialization emphasizes accuracy, relevance, and ethical reporting while working with performance data.
???? Table of Contents
-
Introduction to KPIs and Performance Measurement
-
Role of KPIs in Business Management
-
Understanding Goals, Metrics, and KPIs
-
Types of KPIs Used in Organizations
-
Selecting the Right KPIs
-
Defining KPI Targets and Benchmarks
-
Data Sources for KPI Tracking
-
Structuring KPI Data for Reporting
-
Tracking Individual and Team Performance
-
Department-Wise KPI Tracking
-
Time-Based Performance Monitoring
-
Variance and Deviation Analysis
-
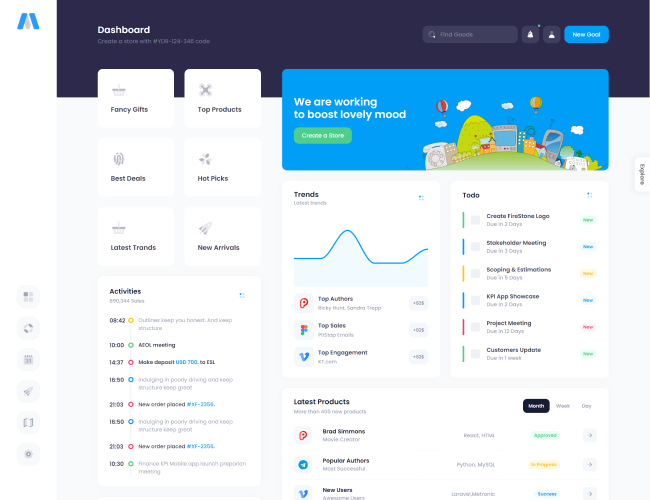
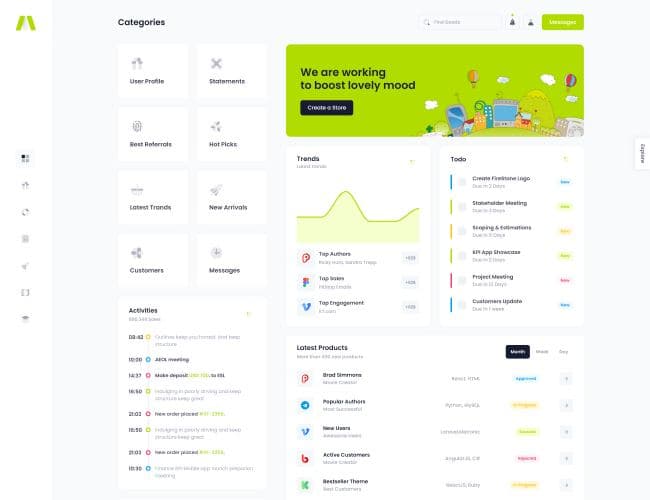
KPI Dashboards and Visual Summaries
-
Reviewing KPI Performance with Management
-
Common KPI Tracking Mistakes
-
Ensuring Accuracy and Consistency in KPIs
-
Documentation and KPI Definitions
-
Ethical Use of Performance Metrics
-
Real-World KPI Tracking Use Cases
-
Career Relevance and Workplace Impact
1. Introduction to KPIs and Performance Measurement
KPIs are measurable values used to evaluate performance against defined objectives. This section introduces learners to the concept of performance measurement and explains why organizations use KPIs to track progress and results.
Learners understand the difference between general data and performance-focused metrics.
2. Role of KPIs in Business Management
KPIs support planning, monitoring, and decision-making. Managers use KPIs to evaluate whether strategies and operations are producing expected results.
This section explains how KPIs influence reviews, goal setting, and corrective actions.
3. Understanding Goals, Metrics, and KPIs
Not all metrics are KPIs. Learners understand the relationship between business goals, supporting metrics, and KPIs.
This clarity helps avoid unnecessary or misleading performance indicators.
4. Types of KPIs Used in Organizations
Organizations track different KPIs depending on their function. Learners are introduced to common KPI categories such as operational KPIs, financial KPIs, productivity KPIs, and quality-related KPIs.
5. Selecting the Right KPIs
Choosing the wrong KPIs can lead to poor decisions. Learners understand how KPIs are selected based on relevance, measurability, and alignment with business objectives.
This section emphasizes quality over quantity.
6. Defining KPI Targets and Benchmarks
KPIs require reference points. Learners understand how targets and benchmarks are defined and why unrealistic or unclear targets reduce the usefulness of KPIs.
7. Data Sources for KPI Tracking
KPIs rely on accurate data. Learners explore how KPI data is sourced from operational systems, reports, and records.
This section emphasizes data reliability and traceability.
8. Structuring KPI Data for Reporting
Well-structured data supports consistent tracking. Learners understand how KPI data is organized for reporting, comparison, and trend analysis.
9. Tracking Individual and Team Performance
KPIs are often used to track individual and team performance. Learners understand how performance is measured at different levels without creating confusion or bias.
10. Department-Wise KPI Tracking
Different departments track different KPIs. Learners explore how KPIs vary across HR, sales, finance, operations, and support functions.
11. Time-Based Performance Monitoring
Performance is reviewed over time. Learners understand how KPIs are tracked daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly and how trends are identified.
12. Variance and Deviation Analysis
KPIs are most useful when deviations are identified. Learners understand how variance analysis highlights performance gaps and areas requiring attention.
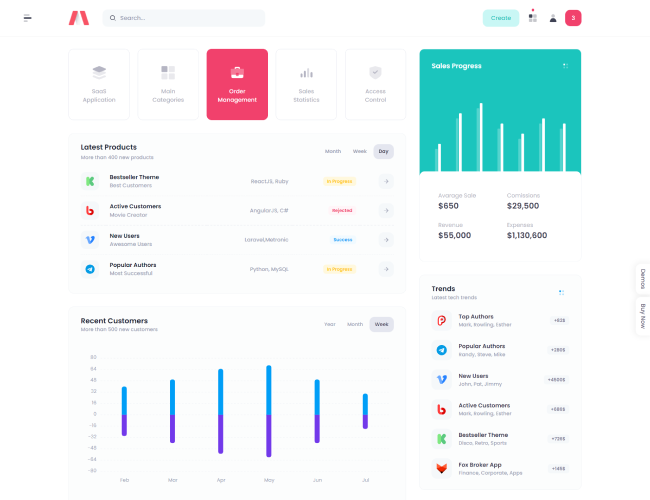
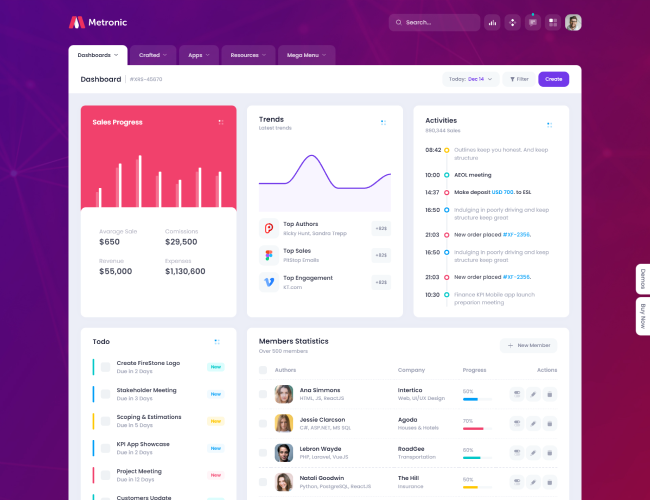
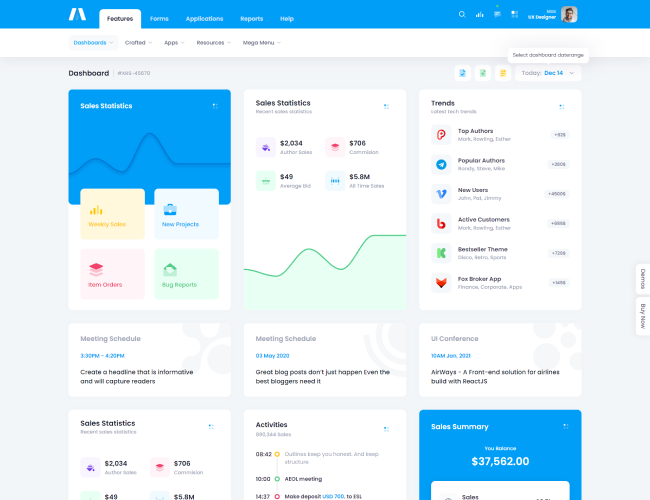
13. KPI Dashboards and Visual Summaries
Visual summaries help management review performance quickly. Learners understand how KPIs are presented using tables, charts, and dashboards.
The focus remains on clarity rather than visual complexity.
14. Reviewing KPI Performance with Management
KPIs are often discussed in review meetings. Learners understand how performance results are explained, questioned, and interpreted during management discussions.
15. Common KPI Tracking Mistakes
Learners explore common mistakes such as tracking too many KPIs, using unclear definitions, or focusing on numbers without context.
Understanding these pitfalls improves reporting quality.
16. Ensuring Accuracy and Consistency in KPIs
Inconsistent KPIs reduce trust. Learners understand how standard definitions, validation checks, and disciplined processes ensure reliable performance tracking.
17. Documentation and KPI Definitions
Clear documentation ensures continuity. Learners understand the importance of maintaining KPI definitions, formulas, and assumptions for long-term tracking.
18. Ethical Use of Performance Metrics
KPIs influence behavior. Learners understand the ethical responsibility involved in designing and reporting performance metrics fairly and transparently.
19. Real-World KPI Tracking Use Cases
Practical scenarios demonstrate how KPI tracking supports performance reviews, planning, and improvement initiatives in organizations.
20. Career Relevance and Workplace Impact
KPI and performance tracking skills are valuable in roles such as MIS executive, analyst, coordinator, and team lead. Professionals who understand KPIs contribute more effectively to performance-driven environments.
? Expected Learning Outcomes
After completing this specialization, learners are expected to:
-
Understand how KPIs are defined and used
-
Track and report performance accurately
-
Support management reviews with reliable data
-
Avoid common KPI reporting mistakes